FAQ 
Mandarin is one of the oldest language in the world, is spoken
by billians people.
Why Mandarin?
Mandarin is one of the oldest languages in the world, and is
the most commonly spoken of the Chinese languages (throughout
the majority of China, Taiwan and Singapore). With about 1.3 billion
people in the World speaking Chinese (one fifth of the World population),
the importance of the language on a globa-scale cannot be denied.
With mainland China now finally opening up to foreign business
and travellers, there has never been a better time to learn Mandarin.
No matter whether you are keen for your business to take advantage
of the huge opportunities available, or are intrested in the 5
thousand year old culture on the other side of the world, you
will benefit from learning the official language that is used
there; Mandarin.
What is the difference between
Chinese and Mandarin?
The term 'Chinese' can refer to many languages spoken in China
and further afield. Each area may have their own dialect. Whilst
it can be argued that Cantonese is either a language or a dialect,
it is Cantonese that is spoken in Hong Kong as well as some other
areas of China.
However, the official language that is learnt at school in throughout
China and Taiwan in order for people to be able to communicate
with others from different states is Mandarin. All the publications
and goverment papers within China are in Mandarin.
What is the difference between
Traditional Chinese and Simplied Chinese?
Traditional Chinese is the written form of the language used
in Hong Kong and Taiwan, the writing having been passed down throughout
history with little change. Simplified Chinese is used in mainland
China. Changes have been made to some characters since 1950 in
order to make them easier to write.
While speaking, there's no difference between them, with both
understandable to each other. Examples of differences between
Traditional and Simplified characters are shown below:
| English |
Traditional Chinese |
Simplified Chinese |
| Visa |
|
|
| Simple |
|
|
If you are interested in traditional Chinese brush writing and
painting, the text is most commonly and traditionally written
in Traditional Chinese characters.
What is Pinyin?
Pinyin is a method of Chinese romanisation, the purpose of which
is to teach pronunciation. Chinese characters can be represented
in Pinyin, having the benefit of enabling learners of the language
to be able to quickly learn the pronunciation of new characters.
As an example, in the table below you can see a variety of Chinese
characters alongside their Pinyin representation. You can also
hear how the character is pronounced. It should be noted that
Mandarin is a tonal language and the tone of the character is
also represented within Pinyin.
| English |
Mandarin |
PinYin |
Voice |
| He |
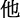 |
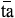 |
 |
| home town |
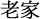 |
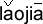 |
 |
| His home town is Beijin. |
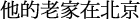 |
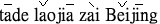 |
 |
What is the most common problem
of learning Mandarin as a second language?
Whilst grammar within Mandarin, compared to English, is relatively
simple, the fact it is a tonal language can cause problems. Each
character is pronounced with one of five different tones, each
with different relative pitch changes as illustrated below:
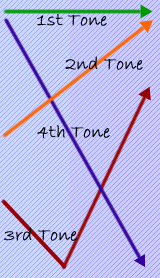
(The fifth tone is a normal, neutral tone.)
The incorrect use of tone can result in characters having totally
different meanings. So, getting the tones right is often the single
most important thing for a new learner of Mandarin. Some examples
are listed below:
What should I prepare for
learning Mandarin?
Nothing!
I can provide all of the materials that you need and will also
guide you through the best way to learn. Apart from being willing
to learn, there is nothing else you will need to prepare.
|